What is an Oort cloud?
What is an Oort Cloud?
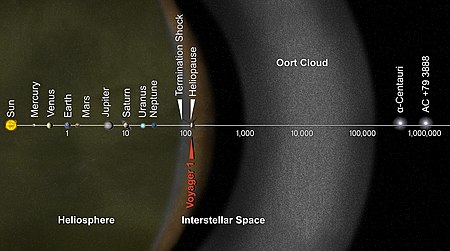
The Oort Cloud is a theoretical cloud of icy solid objects proposed to revolve around the sun in the Interstellar space. The Oort Cloud is beyond Heliosphere (a bubble like substance outside the orbit of Pluto) in Interstellar space (a physical space beyond the influence of any star). It is named after Jan Oort, who first theorized its existence.
What is the story of origin of Oort cloud?
For thousands of years, astronomers have watched comets travel close to the Earth. In this time, their observations led to many paradoxes regarding the origin of comets. And if their surfaces vaporize before reaching the sun, this means they have been formed farther away, where they would have existed for a long time. So the observations led to the theory that far beyond the planetary section, there is a cloud of icy material and rocks where most of the comets come from. But its existence still remains unproven (And so it is called a theoretical cloud). Jan Oort suggested that beyond 1,00,000 AU (Astronomical Units), there is a reservoir which sends ecliptic (short-period) and isomorphic (long-period) comets from their aphelia (longest distance from the sun).
What is Oort cloud's structure and composition?
Astronomers have learned a great deal about its structure and composition.
The Oort Cloud occupies a vast space up to 2,000 AU to as far as 20,000 AU. The region can be sub-divided into a spherical outer Oort Cloud and a torus-shaped inner Oort Cloud. The outer Oort Cloud is weakly bounded to the sun and supplies on isomorphic comets. The inner Oort Cloud (also known as Hills Cloud) is seen to supply ecliptic comets to the planetary system and to the outer Oort Cloud too. The Oort Cloud has more than a trillion objects larger than 1 km. It's total mass is not known but assuming it by Halley's comet (a long period comet), roughly the mass is 3x10^25 kg. The mass of inner Oort Cloud is not yet characterized.
Coming towards composition, seeing comets we understand that the Oort Cloud consists of ices such as water, methane, ethane, carbon monoxide, hydrogen cyanide, etcetera. Study of asteroids say that the population of Oort Cloud consists roughly 0.5% of asteroids.
What are the tidal effects of Oort cloud?
The question now comes that the comets are 1000's of AU away, then how do they enter the planetary system?
This is due to the tidal force exerted by the milky way. Just as the moon's tidal force reforms Earth's oceans, the Galactic tide (Tide of Galaxy) distorts the orbits of bodies in the outer solar system. In the inner parts of our solar system, its effect is negligible due to the strong gravity of the sun; but in the outer reaches, Milky Way's gravitational field has great effects. The Galactic tidal forces stretch the orbit of Oort Cloud far away from the sun than it is, and so the particles come out in our planetary system isolated by the Oort Cloud and trapped in Sun's gravity. Now the comet will continue to revolve the sun until it melts completely.
Some scholars also theorize that the Galactic tide may have contributed in the formation of the Oort Cloud by increasing the perihelia (shortest distance from the sun) of objects.
What are future explorations of Oort cloud?
Voyager 1 is the fastest and farthest probe to escape the solar system. But still it may take 300 years to reach the Oort Cloud. But scientists announced that in 2025, it will become non functional due to lack of power supply from thermoelectric and solar generators.
Some posts have been marked as "Old Posts". Less likely, but they might have out dated or incorrect information, ugly looking bits of code, no labels, etc. Don't get me wrong, many of these posts are top-notch and interesting too.
I thought it would be better not to delete or revamp these posts, even if they suck. The bitter truth is that old works always suck, but I take that as a positive tool to convey that I am growing. Besides there's no better way to showcase my journey without these old, messy, poorly written posts!
I thought it would be better not to delete or revamp these posts, even if they suck. The bitter truth is that old works always suck, but I take that as a positive tool to convey that I am growing. Besides there's no better way to showcase my journey without these old, messy, poorly written posts!
Old Post